Who Else Wants Info About How To Check Ram Memory In Linux

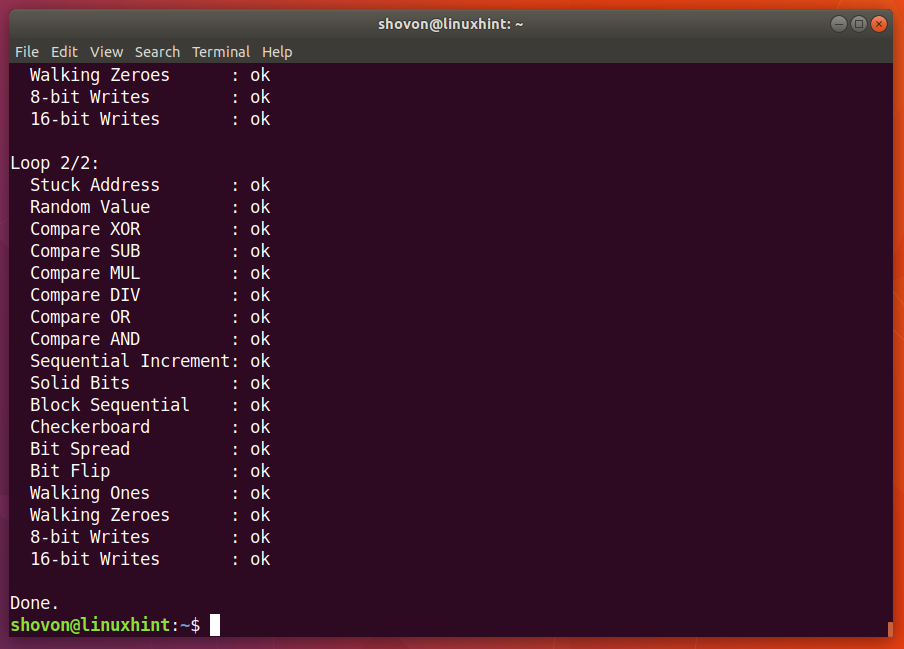
One of the simplest and most commonly used methods to check the ram in a linux system is by using the free command.
How to check ram memory in linux. We can filter out the file using the grep command or egrep command as follows: How to check your cpu in linux. It provides necessary utilities of the underlying memory hardware,.
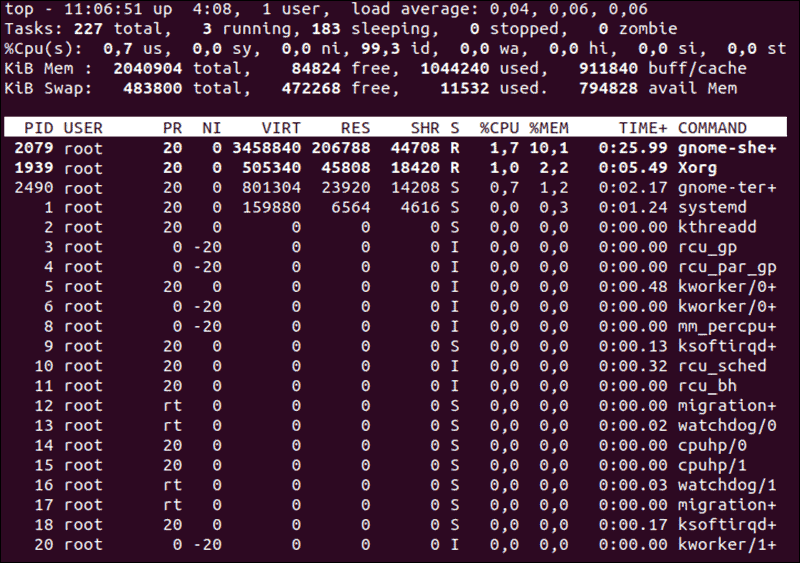
Table of contents. The memory management (mm) subsystem stands as a vital cornerstone in the linux kernel. The top command to display current ram use.
How do you measure the memory usage of an application or process in linux? This command provides a concise. There are a variety of linux commands.
As you can see, the output is divided into two categories : By using free, you are provided with the following information : This command is mainly used for checking.
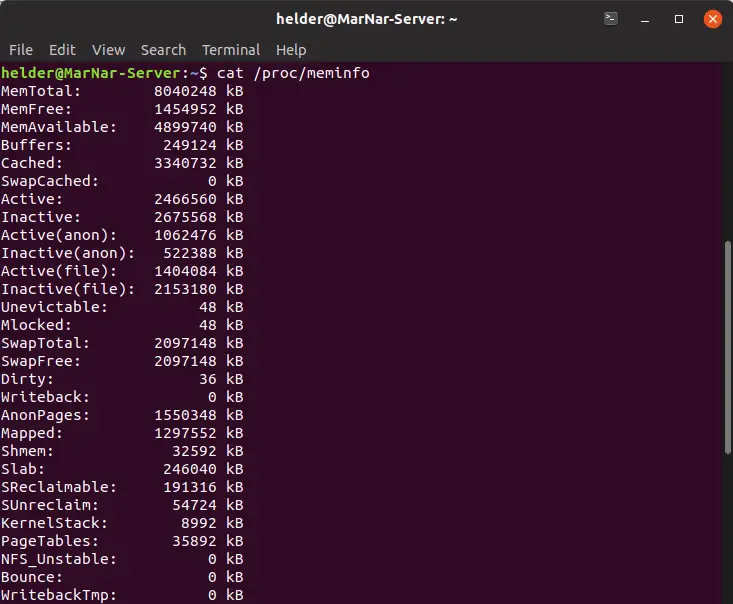
The most popular command in order to check your ram on linux is to use the “free” command. The /proc/meminfo file tells you about memory usage on the server. Sometimes, we might need to check for total memory size on a server running linux or we might need to use memory stats in shell scripts.
Memory (the actual ram) and swap (also called virtual memory). This file is used by the free command and.
The free command is a commonly used utility in linux to view information about system memory usage, including ram. The free command is the most classic terminal based. Look out for “ type:
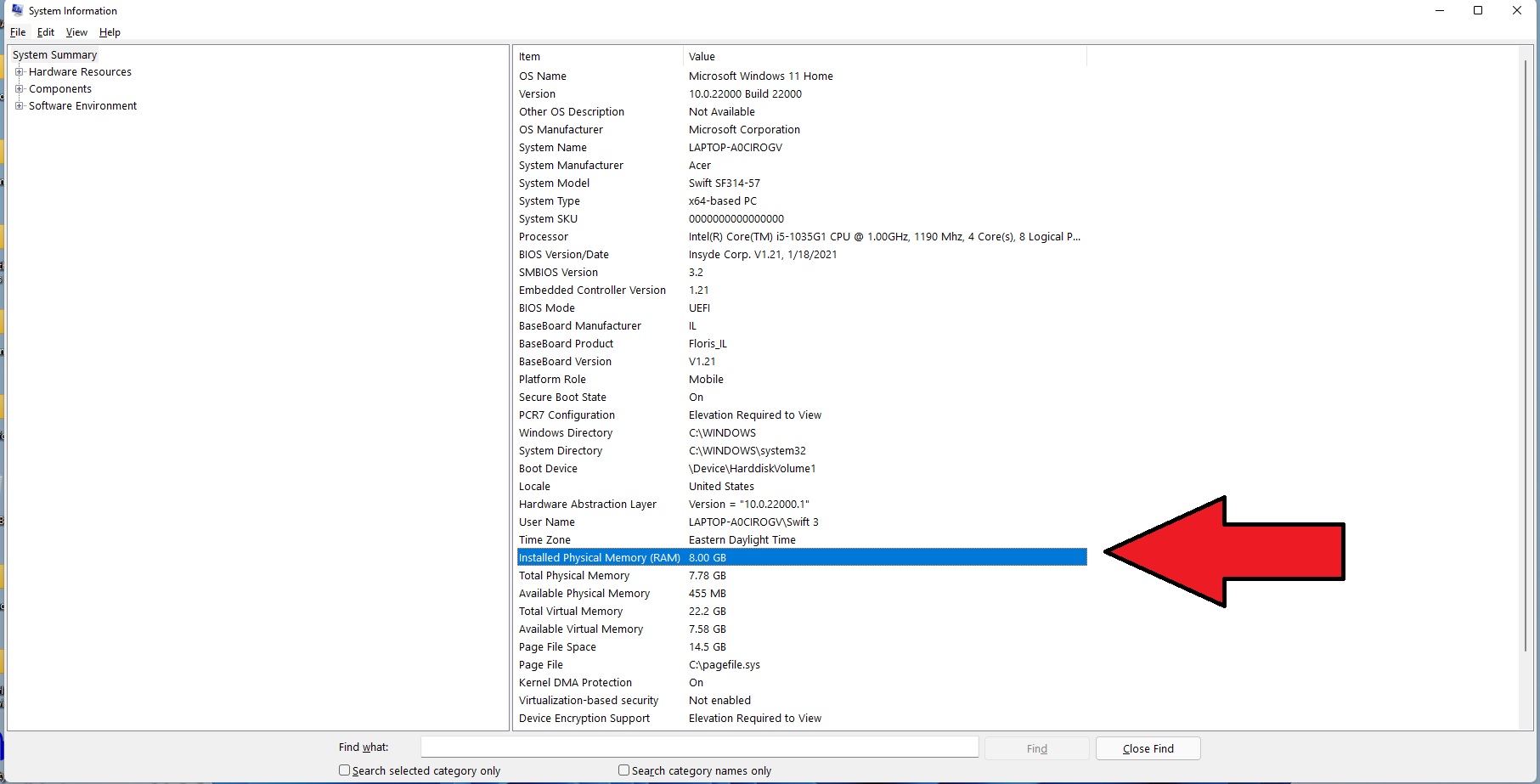
The procedure to find and show random access memory (ram) in gigabytes (gb) is as follows: Here is the list of the top 5 commands that can be used to find linux ram size in linux. Manually check /proc// /proc/ [pid]/statm.
Open the linux terminal application. Since the free command is the most widely used and, without any doubt, the most helpful, we will mention its usage first. From the blog article of understanding memory usage on linux, ps is not an.
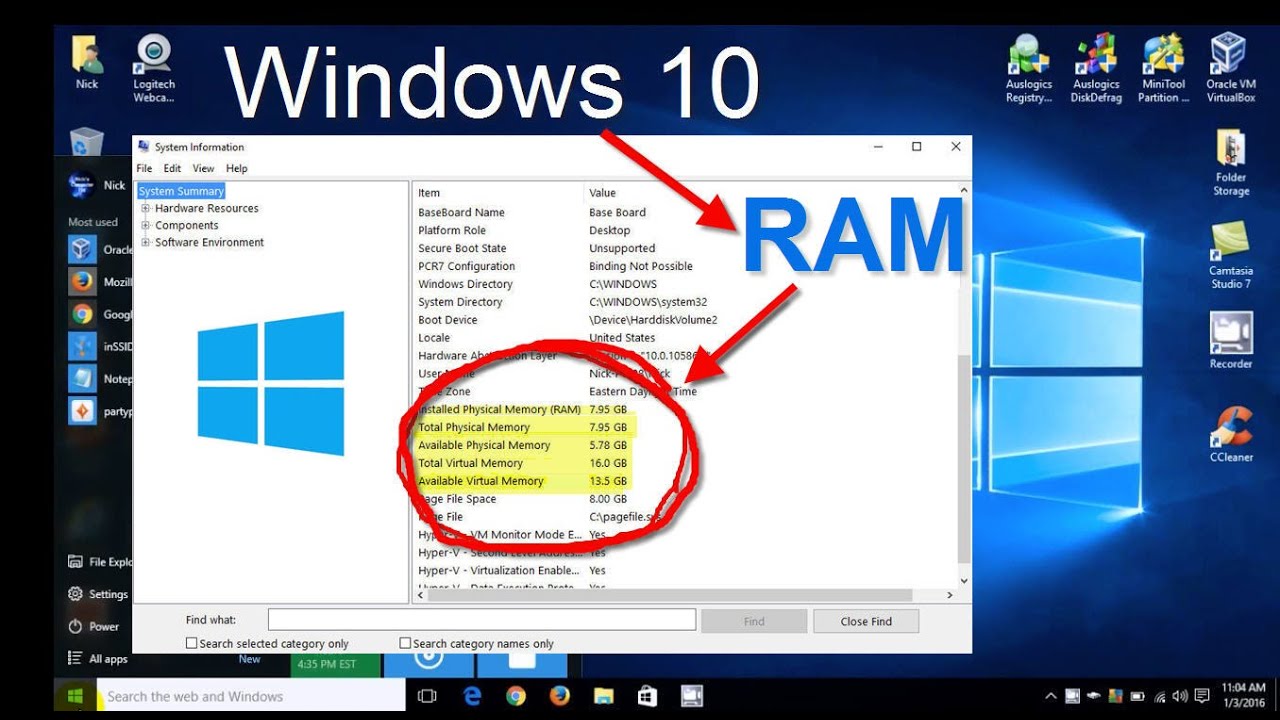
Let us see all examples and. Use /proc/meminfo file to find ram size in linux. This means that you get to see the ram size in gb, mb etc instead of in bytes.